What is Orchialgia?
Orchialgia, also known as chronic testicular pain or chronic scrotal contents pain is a condition where a man has persistent pain in the scrotum that is not caused by any identifiable organic cause. This may develop on its own or following infection, trauma, inflammation or surgery (vasectomy, hernia repair). Pain can also be referred to the scrotum even though the actual source of pain is coming from somewhere else. Examples can include a kidney stone or a spinal problem that traps or inflames the nerves.
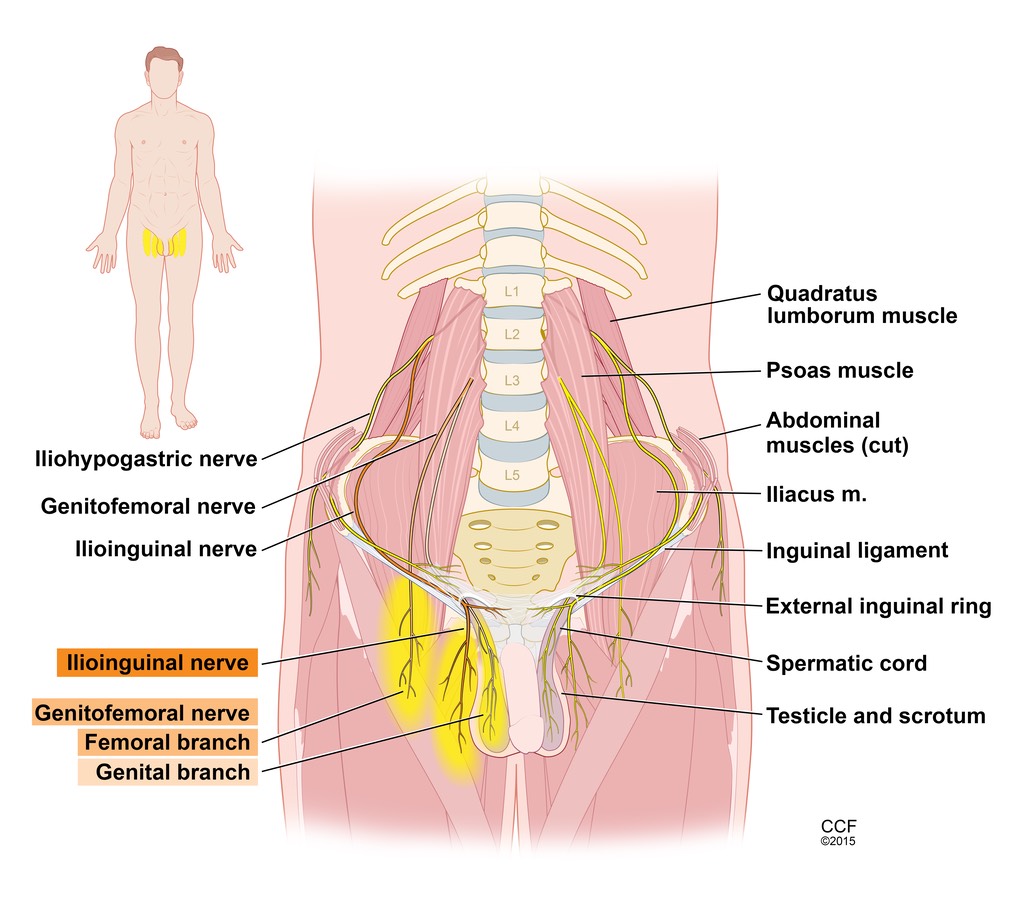
Therapy for orchialgia
Any testicular cause should be diagnosed and treated (eg. infection, hydrocele). Pain due to spasm of the muscles of the pelvic floor can be treated with pelvic floor physical therapy. Otherwise, conservative measures are best to try for at least 3 months. These can include rest, heat, tight fitting underwear and oral anti-inflammatory medications (eg ibuprofen). If pain persists, an important diagnostic test to see whether a Urologist can help is to inject local anesthetic into the spermatic cord (the structure carrying the vas, nerves, blood vessels and lymphatics to the testicle). This "cord block” should anesthetize the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve (see diagram above) and inguinal branches of the ilioinguinal nerve. If a cord block doesn’t eliminate the pain, it is best to pursue further treatment with a pain management physician.
Cord Denervation Surgery for Orchialgia:
If a cord block relieves the pain, microsurgical cord denervation can be curative. In this outpatient surgery, the cord is exposed and using an operating microscope and meticulous microsurgical technique, the blood and lymphatic supply of the testicle are preserved and the remaining structures (which contain the nerves) are transected. For properly selected patients (pain duration > 6 months, failure of all other medical therapies, complete temporary relief with a cord block), over 75% of patients have long term pain relief.